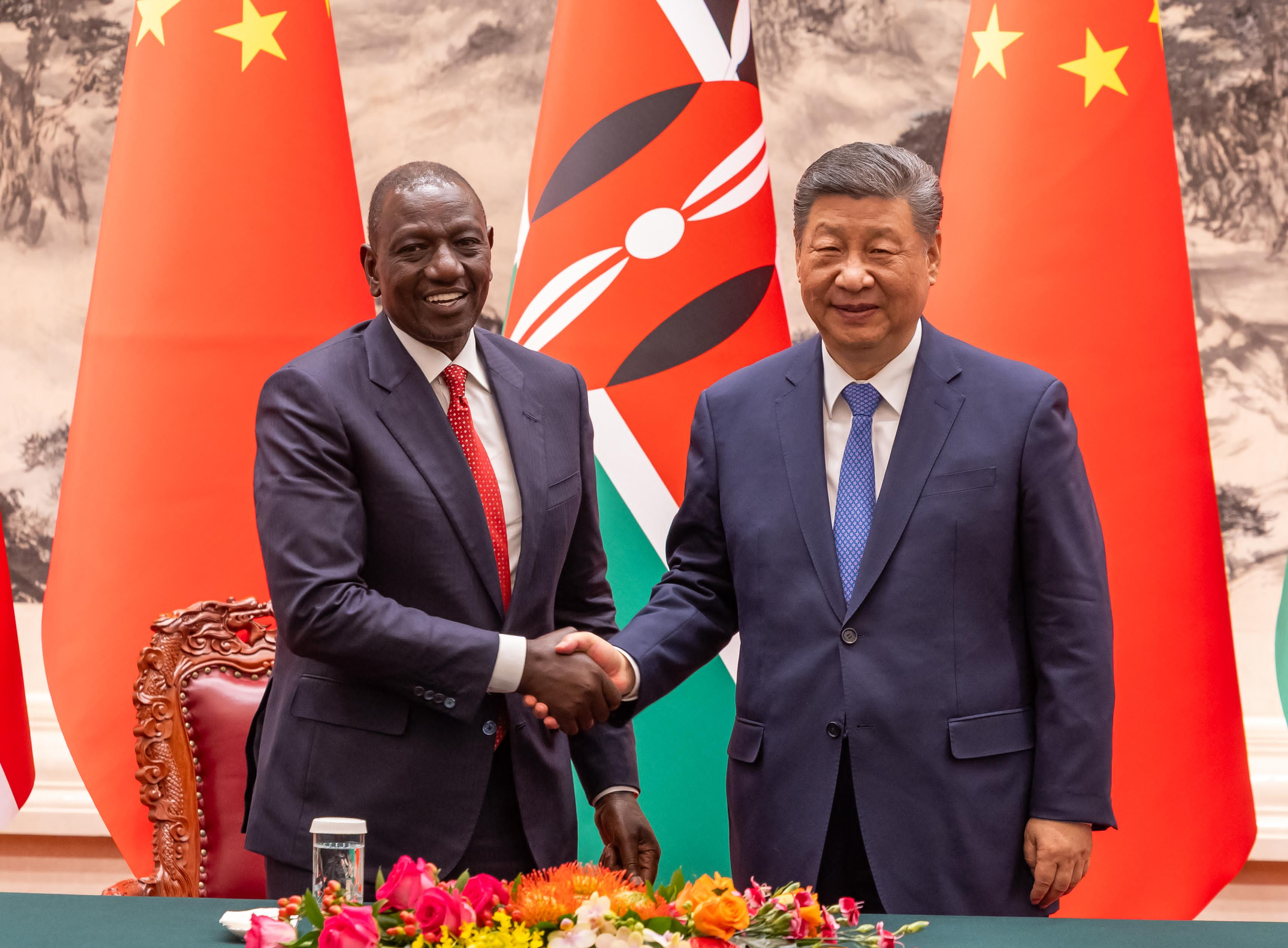

President William Ruto’s state visit to Beijing entered a crucial phase Thursday with a landmark diplomatic and development triumph.
Ruto and his host, President Xi Jinping, witnessed the signing of a comprehensive "Win-Win" framework of agreements.
The event, held at the Great Hall of the People, saw agreements spanning various sectors inked.
At the heart of the agreements is a Memorandum of Understanding (MoU) on Blue Economy, Fisheries, and Maritime Affairs, aligning Kenya with the WTO Fisheries Subsidies Agreement.
This milestone is set to empower coastal communities by promoting sustainable ocean resource management, creating jobs, and boosting exports.
It also positions the country as a leader in harnessing the untapped potential of its marine resources while ensuring environmental sustainability.
The visit also birthed groundbreaking collaborations in science, technology, and innovation.
A new MoU on Scientific and Technological Cooperation fosters partnerships in research, innovation, and technological advancements.
Kenyan scientists, researchers, and tech entrepreneurs now have access to cutting-edge expertise, paving the way for local innovations that can compete on the global stage.
Infrastructure development was the cornerstone of the partnership, with Kenya set to benefit from key projects under the Belt and Road Initiative (BRI).
These include the extension of the Standard Gauge Railway (SGR) Phases 2B and 2C, the dualling of the Rironi-Mau Summit Highway under PPP and 15 CDB-funded rural roads.
Also included is the financing for dualling of the Northern Bypass, dualling of Kiambu Road to Northern Bypass, Nithi Bridge construction, financing of Intelligent Traffic Management System (ITMS) and expansion of Eldoret City Roads.
Others are the construction of Eldoret Eastern by-pass, dualling of Cheplasgei–Maili Tesa, upgrading of Mosoriot–Moiben Junction-Chepkoilel University (Kuinet) and Moiben Junction-Marura centre.
Some other road projects across the country will also be funded through securitisation strategies.
Additionally, an agreement on railway laws, infrastructure, operation standards, and multimodal transport lays the groundwork for a modern rail network that connects people and markets across the region.
A framework agreement for Phase III of Nairobi’s Intelligent Transport System and improved city junctions to help reduce traffic congestion and enhance urban mobility is also included.
In healthcare, there was an exchange of notes on the feasibility studies for upgrading Londiani and Baringo County Referral Hospitals.
Meanwhile, a framework agreement on irrigation and water management ensures enhanced food security and drought resilience for farmers, addressing challenges posed by climate change.
An MoU on Vocational Education focused on technical training, joint curricula, digital transformation, and enterprise links to ensure TVET graduates are job-ready and aligned with employer needs.
A renewed cultural cooperation program and joint museum initiatives aim to promote tourism and celebrate Kenya’s rich heritage on the global stage.
The National Museums of Kenya and China's Natural History Museum are set to work together towards joint research and exhibitions in a bid to promote tourism and heritage preservation.
A protocol was also signed on hygiene and quarantine standards for Kenya’s aquatic exports to China.
This is aimed at increasing income for local fish farmers while ensuring compliance with international food safety standards.
National broadcaster-KBC and China's Xinhua News Agency inked a deal for enhanced news exchange and dissemination.
This is geared at amplifying Kenya’s voice globally and promoting accurate storytelling about the nation’s progress.
On the other hand, the Kenya News Agency (KNA) is set to benefit from media exchanges, public diplomacy, and Kenya’s visibility on the global stage through a deal with China’s State Council Information Office.
An MoU on capacity development covering leadership training, faculty exchanges, and policy research is set to groom a pipeline of skilled professionals and policy thinkers from the country.
The Implementation Plan for 2025 human resource development also featured.
It will guarantee 670 training slots and seminars for diplomats, officers, and other key personnel, building capacity in public service and governance sectors.
An implementation programme under the 1980 Cultural Cooperation Agreement for 2025–2028 puts Kenyan culture on the global stage and strengthens bilateral ties.
There was also an MoU to build e-commerce laws, promote online business, train entrepreneurs, and support national pavilions, empowering Kenyan businesses to trade globally in the digital marketplace.
An MoU to align policies, support innovation, and train digital talent accelerates Kenya’s transformation into a tech-driven economy, was also penned.
The Ministry ICT is also set to work with China Media Group to foster collaboration on content, technology, and commercial ventures to drive growth in the creative economy while boosting digital exports in another deal signed.
Complementing this, an agreement promoting sustainable manufacturing, agro-processing, and trade competitiveness spurs industrial growth, creates jobs, and enhances Kenya's global trade position will help unlock new markets for tea, nuts, rice, and coffee.
Diplomatic ties were further strengthened through the exchange of notes for constructing Kenya’s Ministry of Foreign Affairs headquarters, bolstering international diplomacy and diaspora engagement.
On environmental sustainability, an MoU for low-carbon development, climate action, and green economy collaboration reinforces Kenya’s commitment to its climate agenda and sustainable development goals.
In the digital realm, a Cyberspace Accord focusing on AI cooperation, data protection, cyber laws, and digital policy exchange ensures Kenya is well-positioned to secure its digital future while fostering responsible innovation.
Further cementing Kenya’s ocean-based potential, an additional MoU deepens investment and growth in the Blue Economy, attracting global interest and creating opportunities for coastal communities.
In preparation for the AI revolution, another agreement focuses on AI infrastructure, safety, and applications, equipping Kenya’s economy and workforce with the tools needed to thrive in a rapidly evolving technological landscape.
The two countries also signed an MoU on immigration-visa processes, anti-smuggling measures, human trafficking prevention, and personnel training.
This is to strengthen Kenya’s border security systems and modernise migration management frameworks.











![[PHOTOS] Ruto launches Rironi-Mau Summit road](/_next/image?url=https%3A%2F%2Fcdn.radioafrica.digital%2Fimage%2F2025%2F11%2F6f6601a6-9bec-4bfc-932e-635b7982daf2.jpg&w=3840&q=100)


